St. Helena
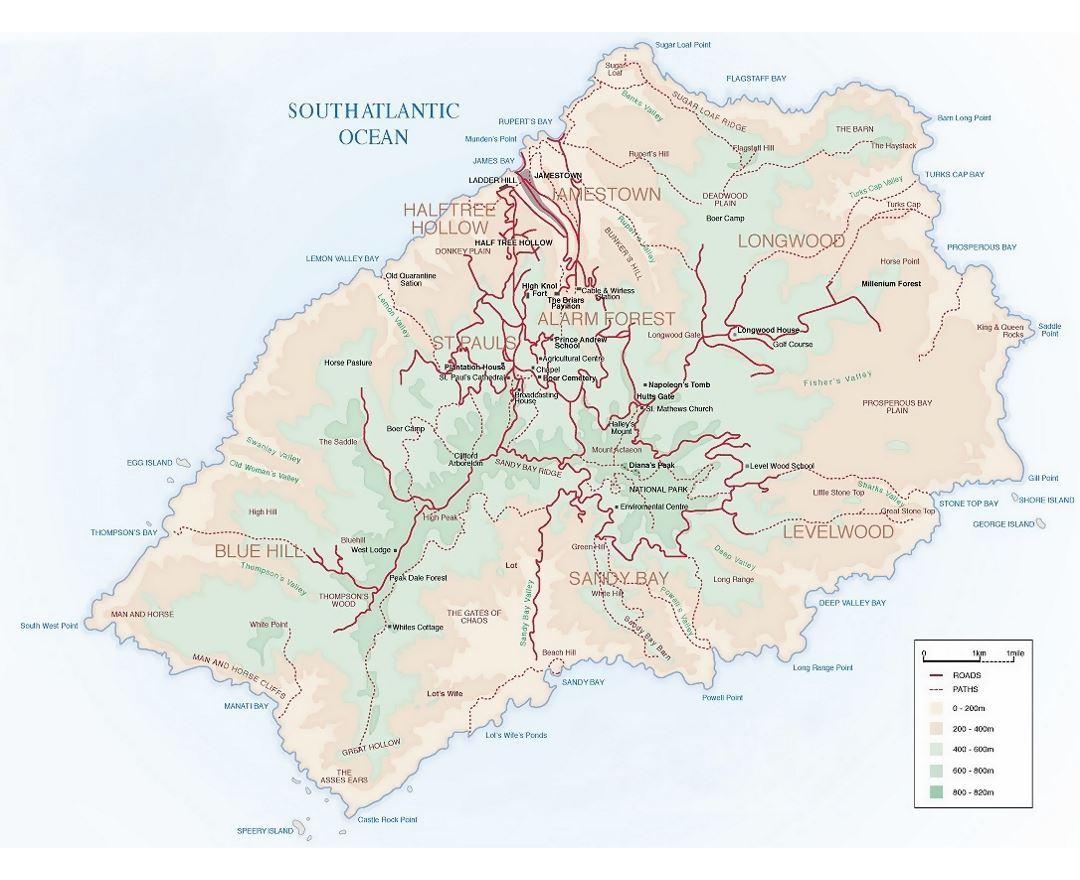
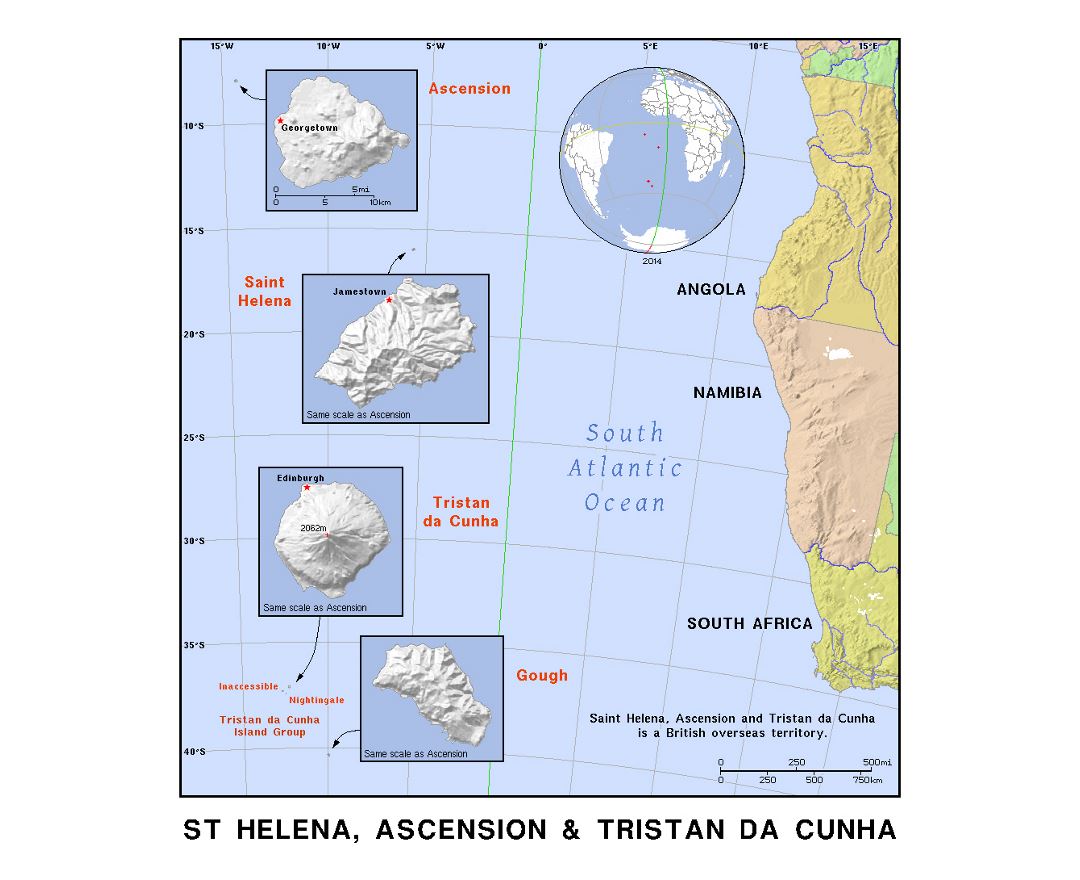
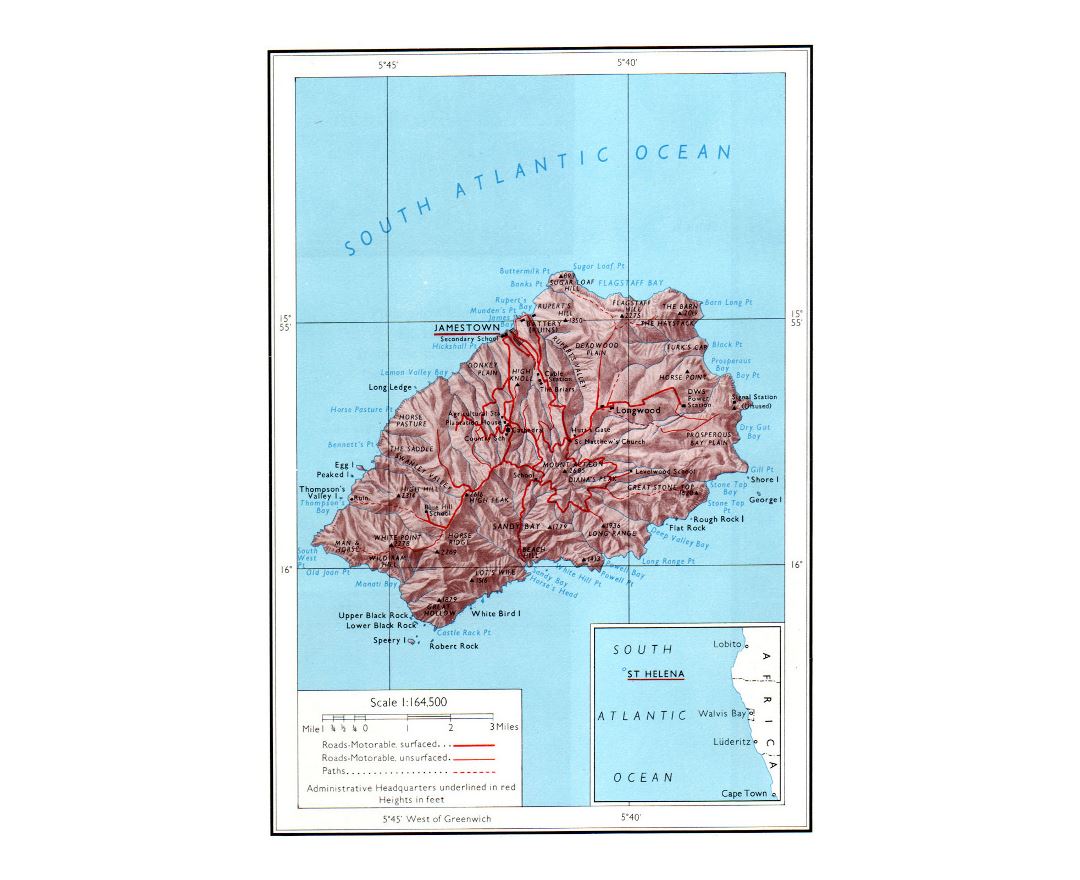
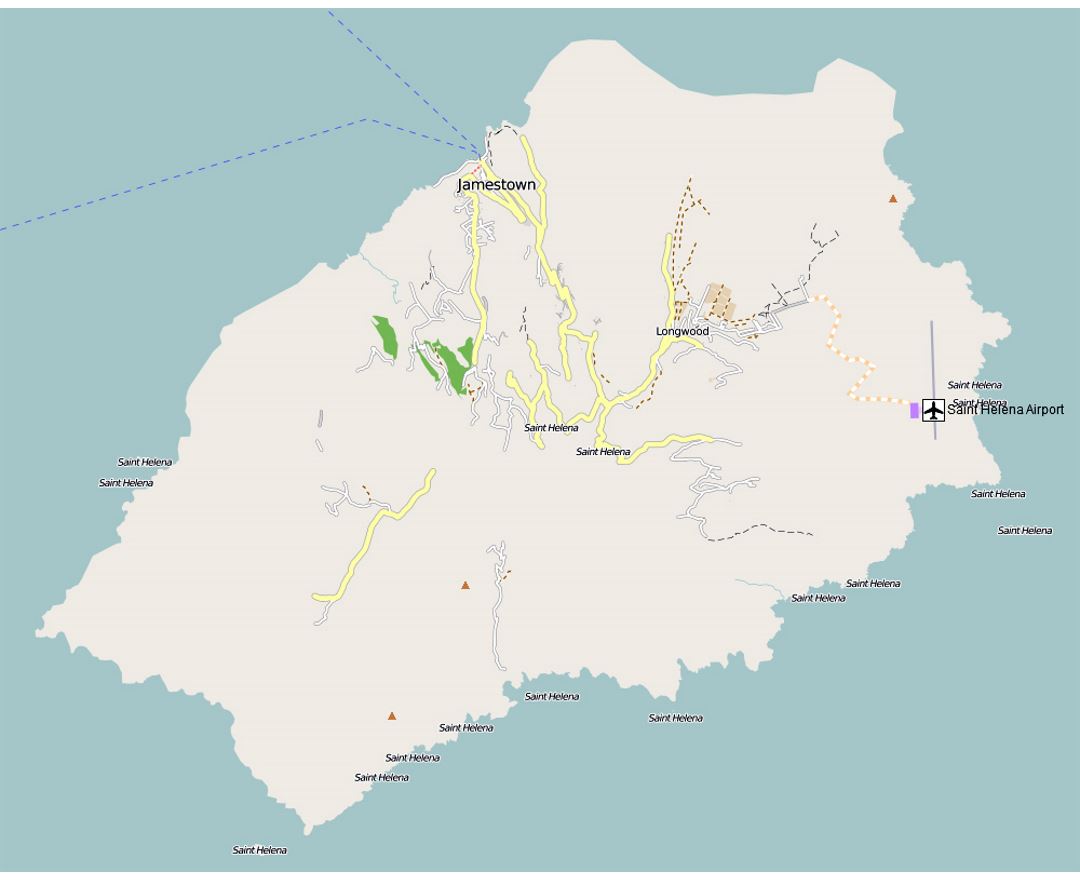
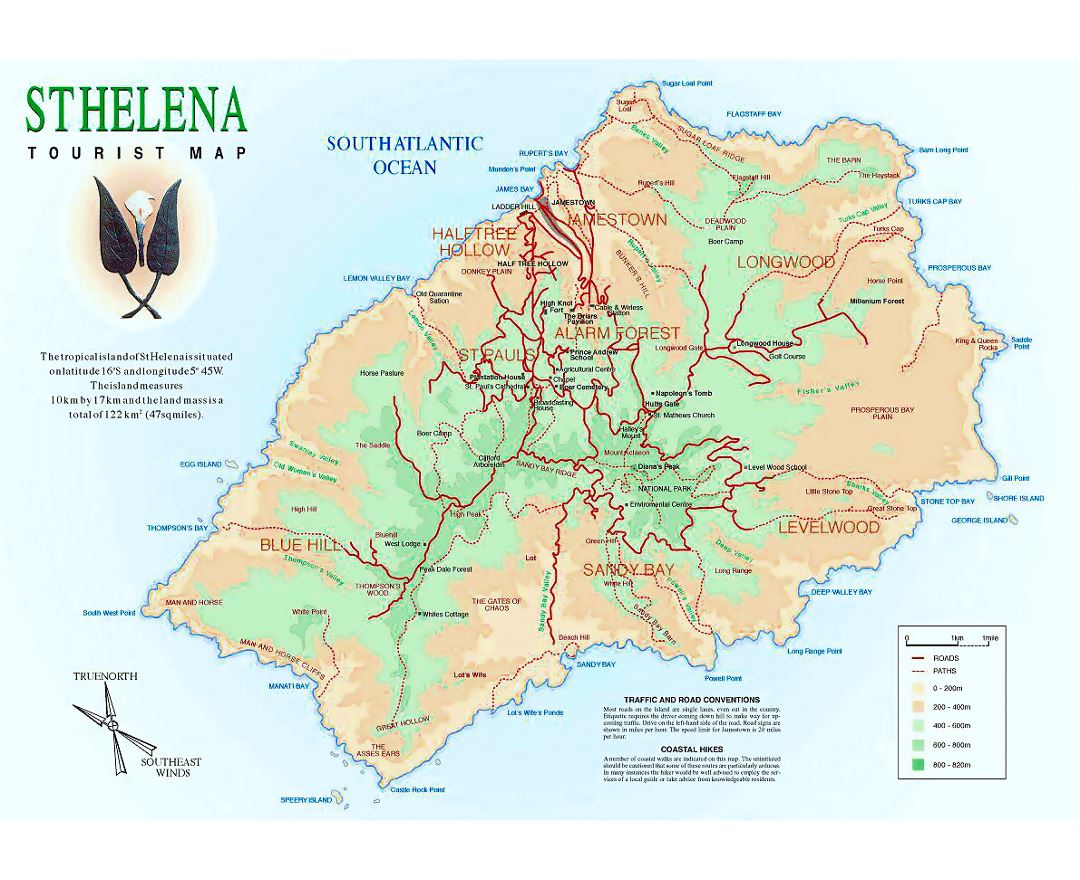
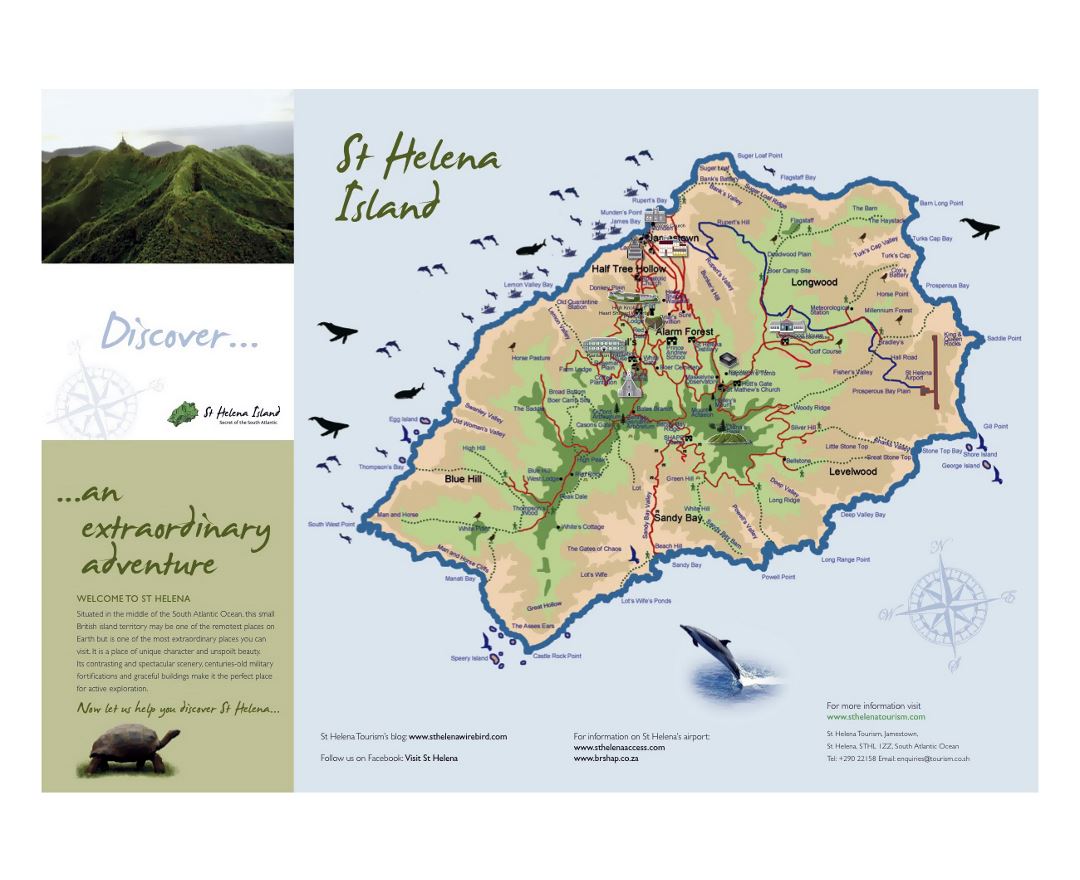
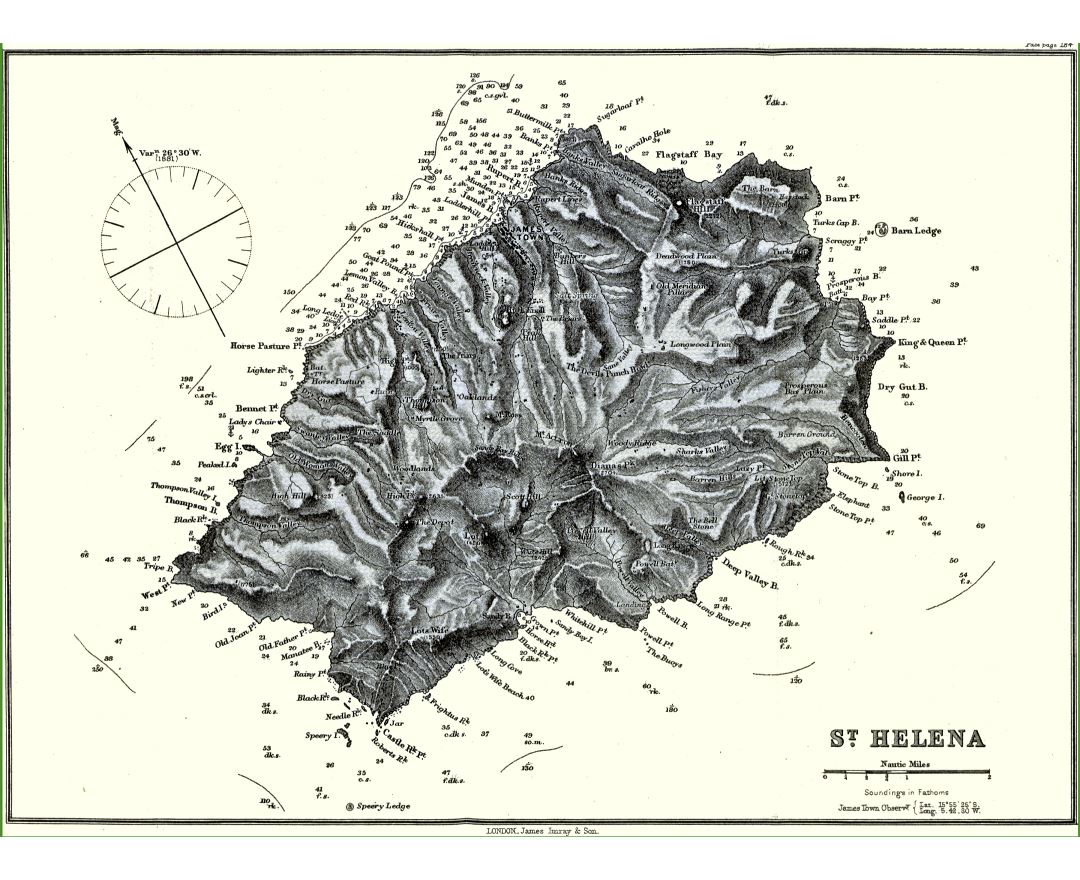
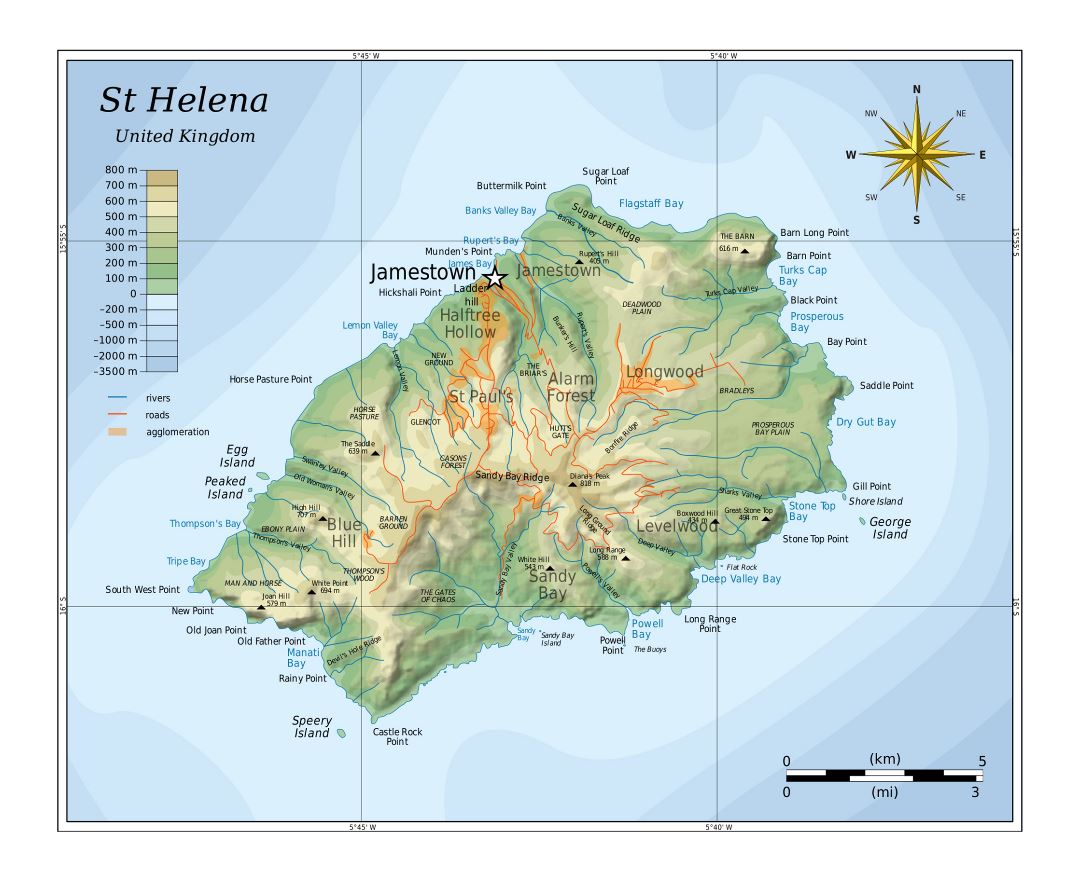
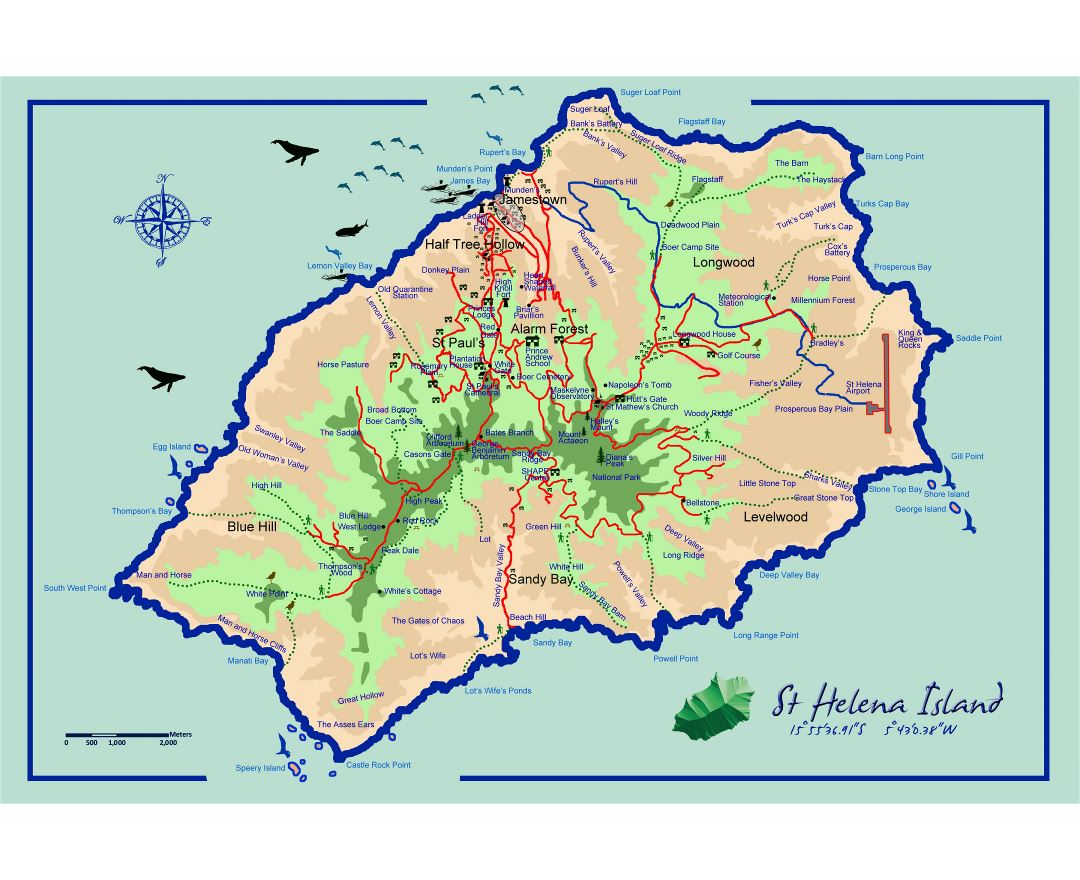
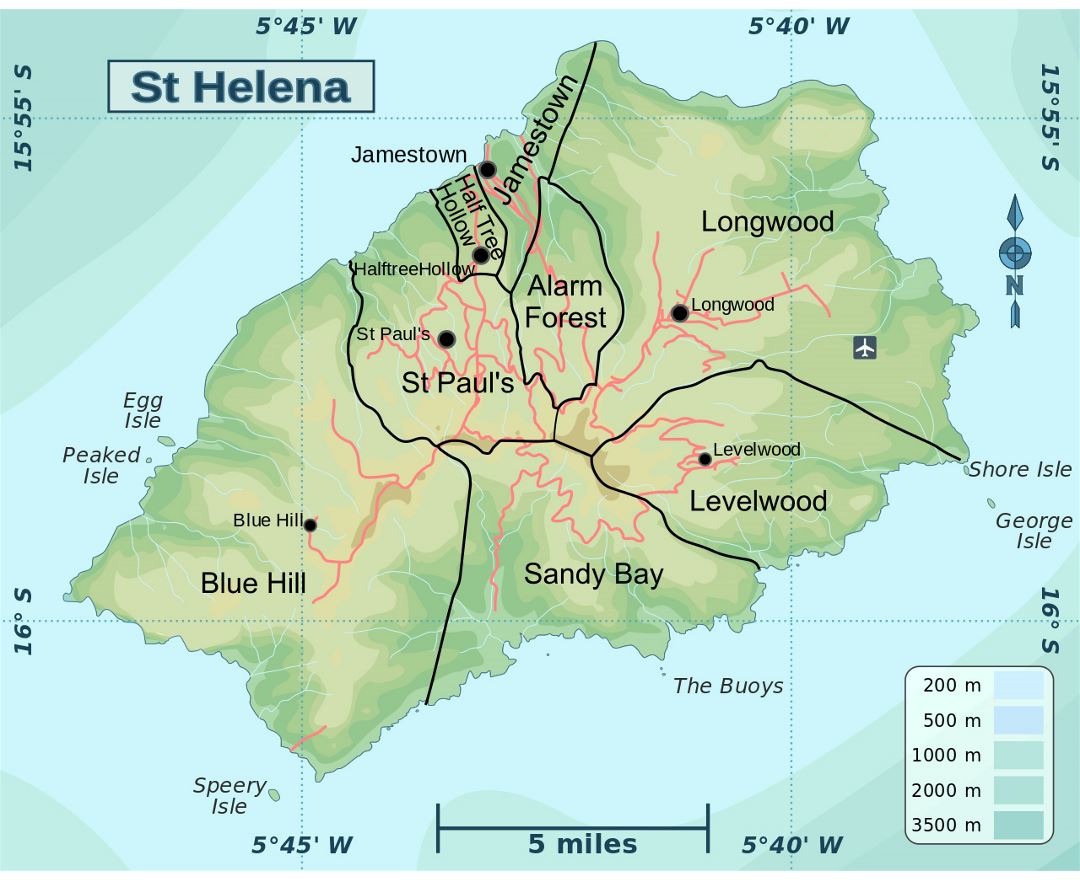
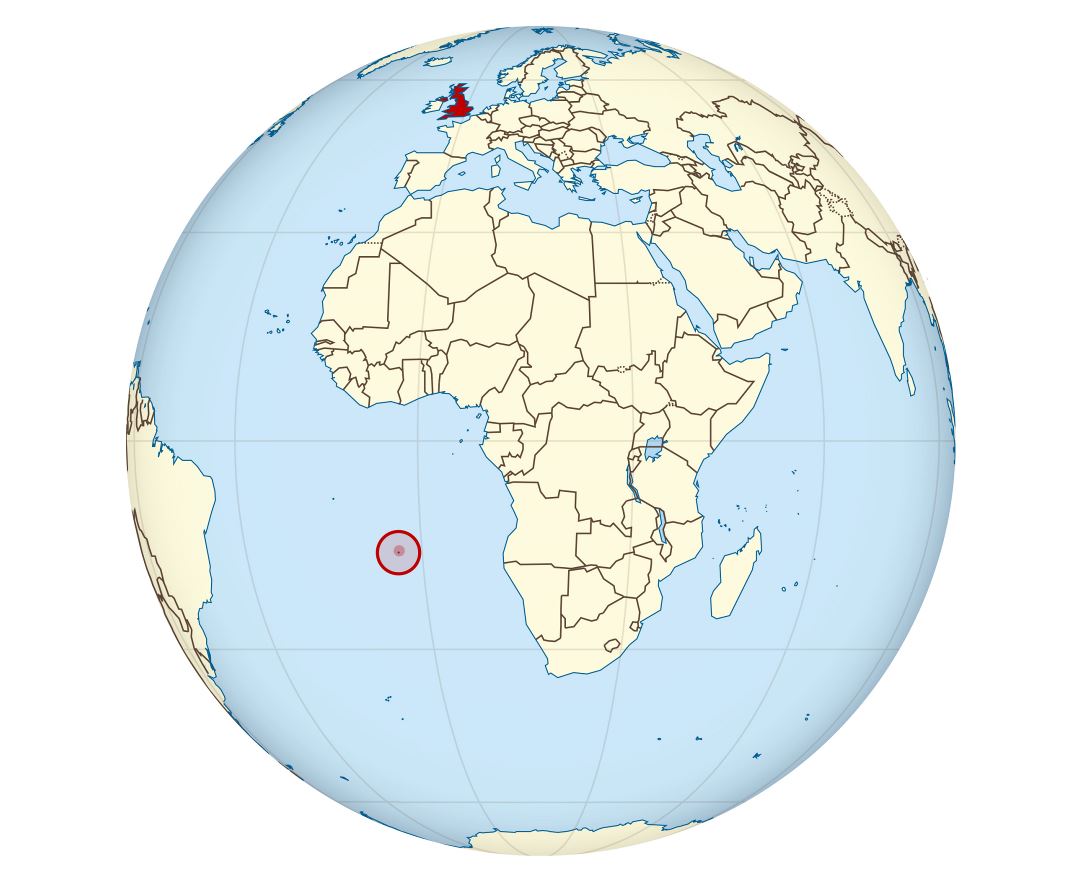
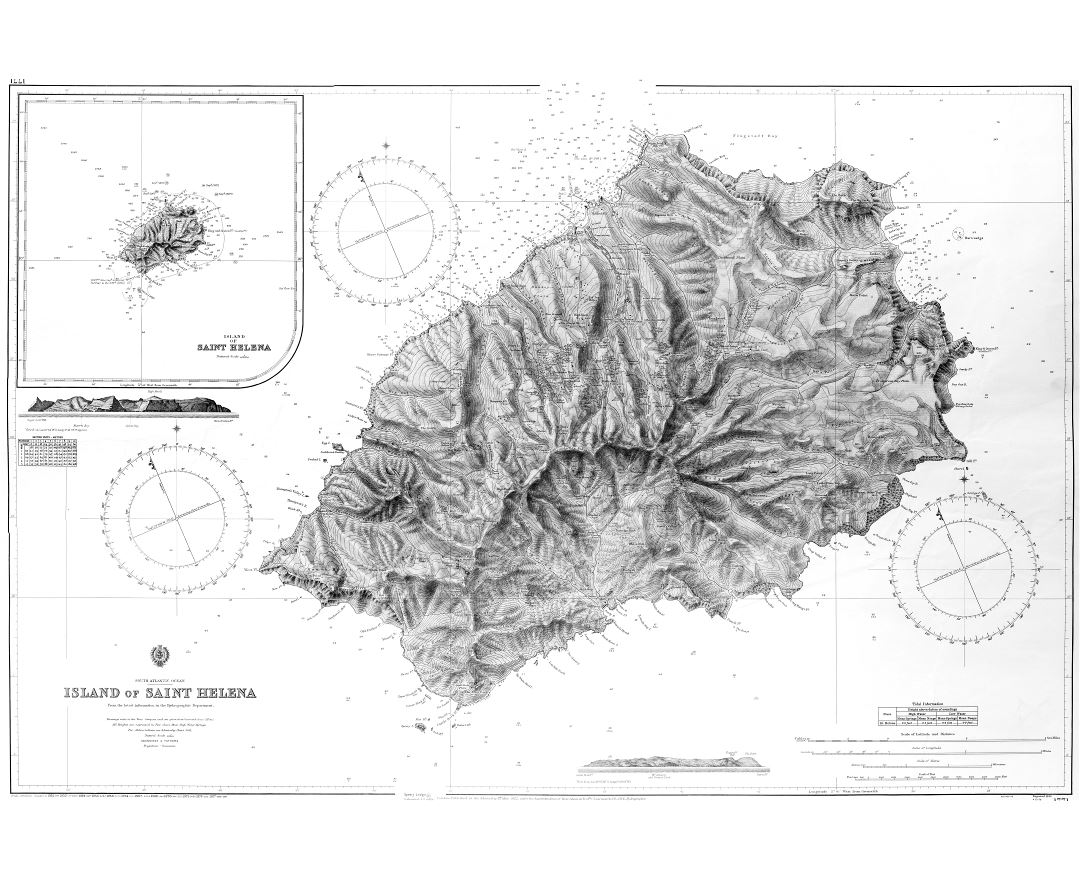
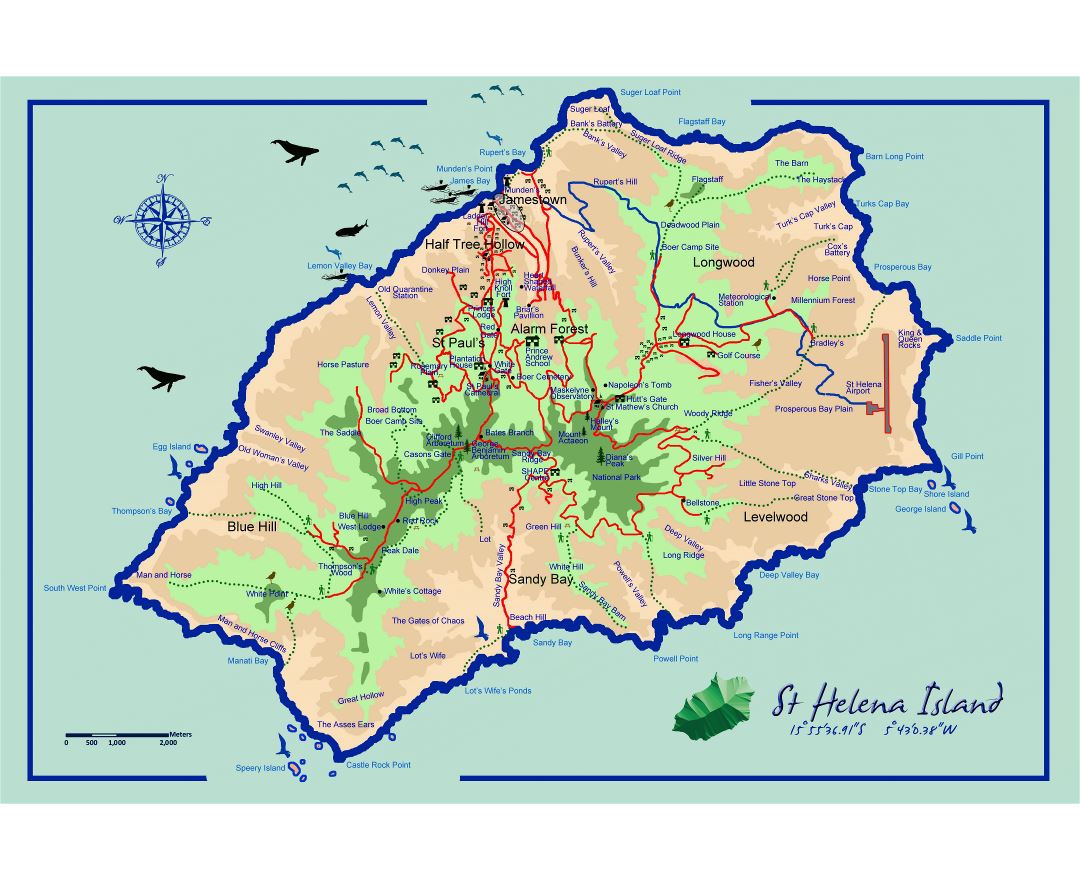
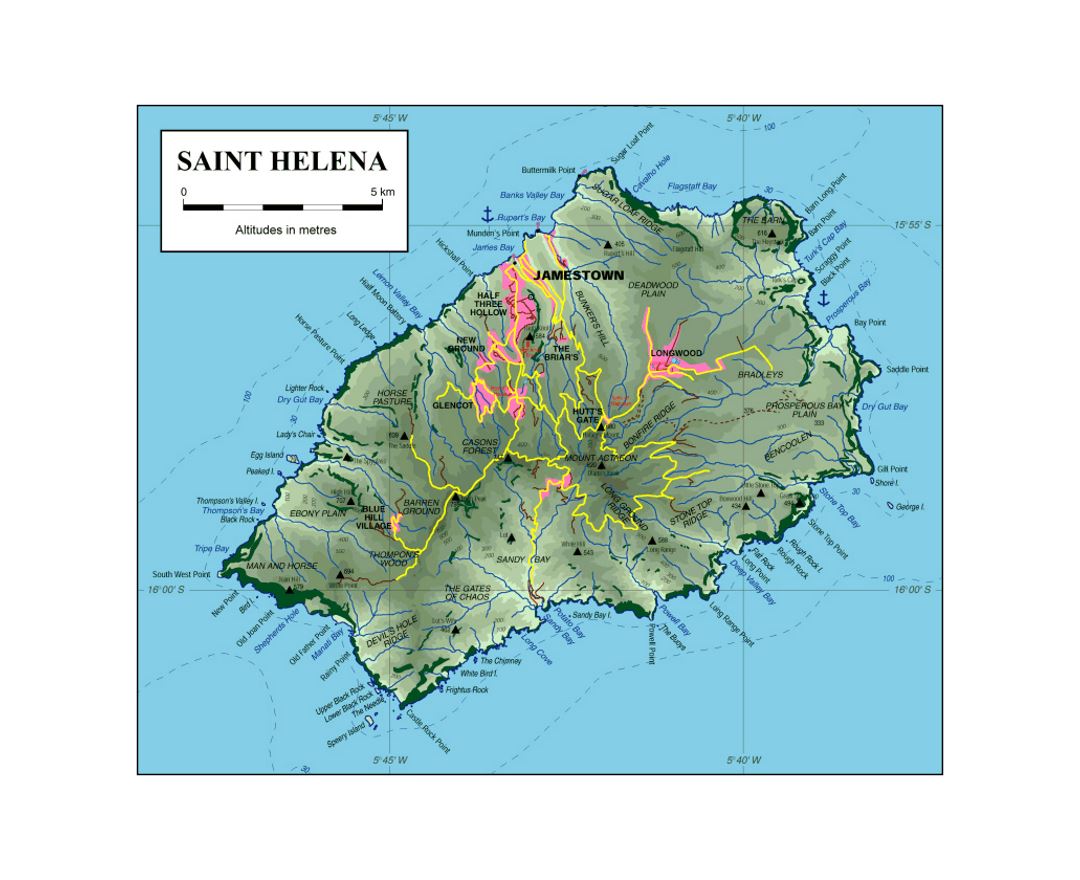
Saint Helena is a volcanic tropical island in the South Atlantic Ocean, 4,000 kilometres (2,500 mi) east of Rio de Janeiro and 1,950 kilometres (1,210 mi) west of the Cunene River, which marks the border between Namibia and Angola in southwestern Africa. It is part of the British Overseas Territory of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha. Saint Helena measures about 16 by 8 kilometres (10 by 5 mi) and has a population of 4,534 (2016 census). It was named after Saint Helena of Constantinople.
The island, one of the most remote islands in the world, was uninhabited when discovered by the Portuguese in 1502. It was an important stopover for ships sailing to Europe from Asia and South Africa for centuries. Napoleon was imprisoned there in exile by the British, as were Dinuzulu kaCetshwayo (for leading a Zulu army against British rule) and more than 5,000 Boers taken prisoner during the second Boer War.
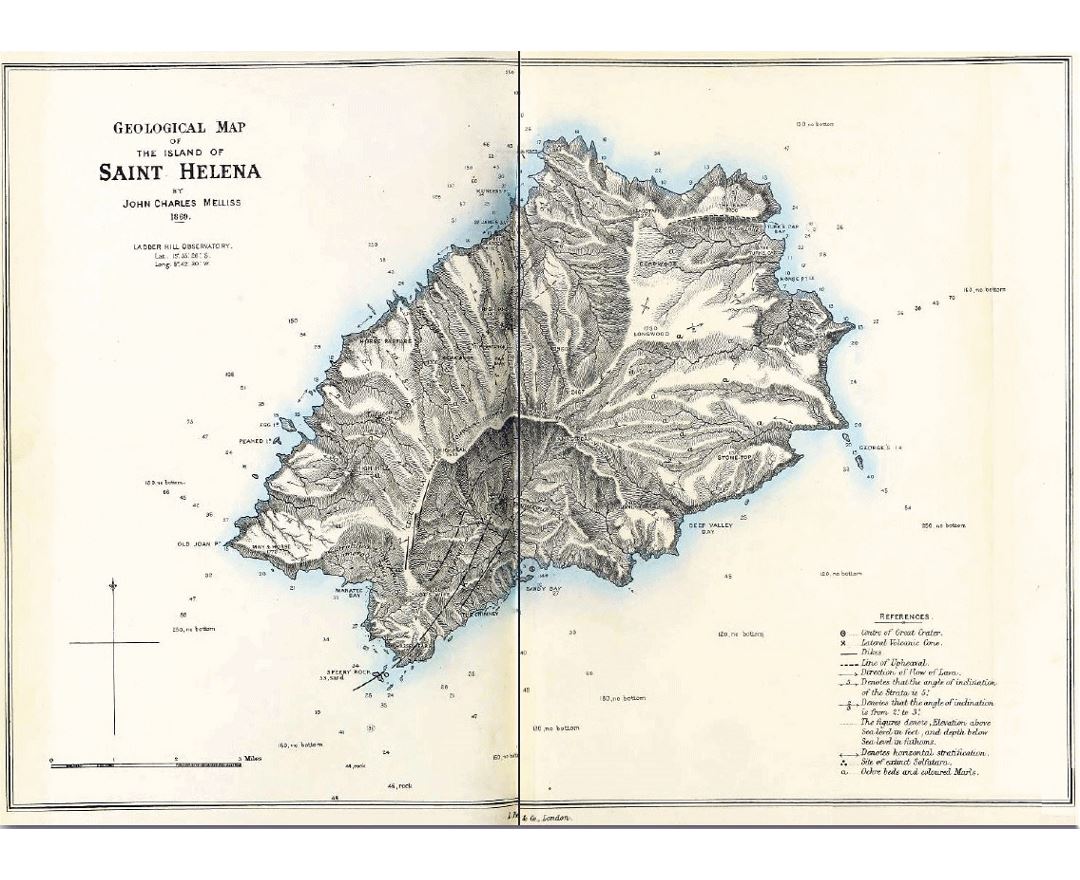
Between 1791 and 1833, Saint Helena became the site of a series of experiments in conservation, reforestation and attempts to boost rainfall artificially. This environmental intervention was closely linked to the conceptualisation of the processes of environmental change and helped establish the roots of environmentalism.
Saint Helena is Britain's second-oldest remaining overseas territory after Bermuda.