Czech Republic
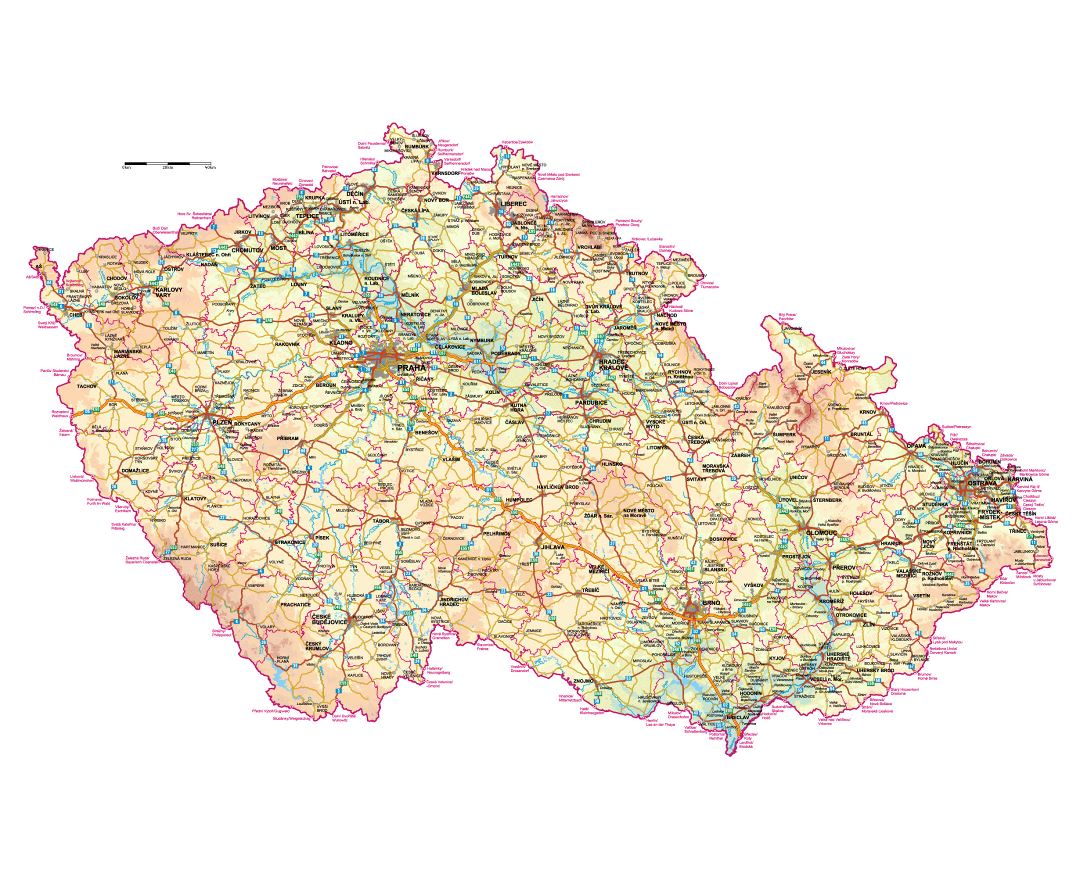
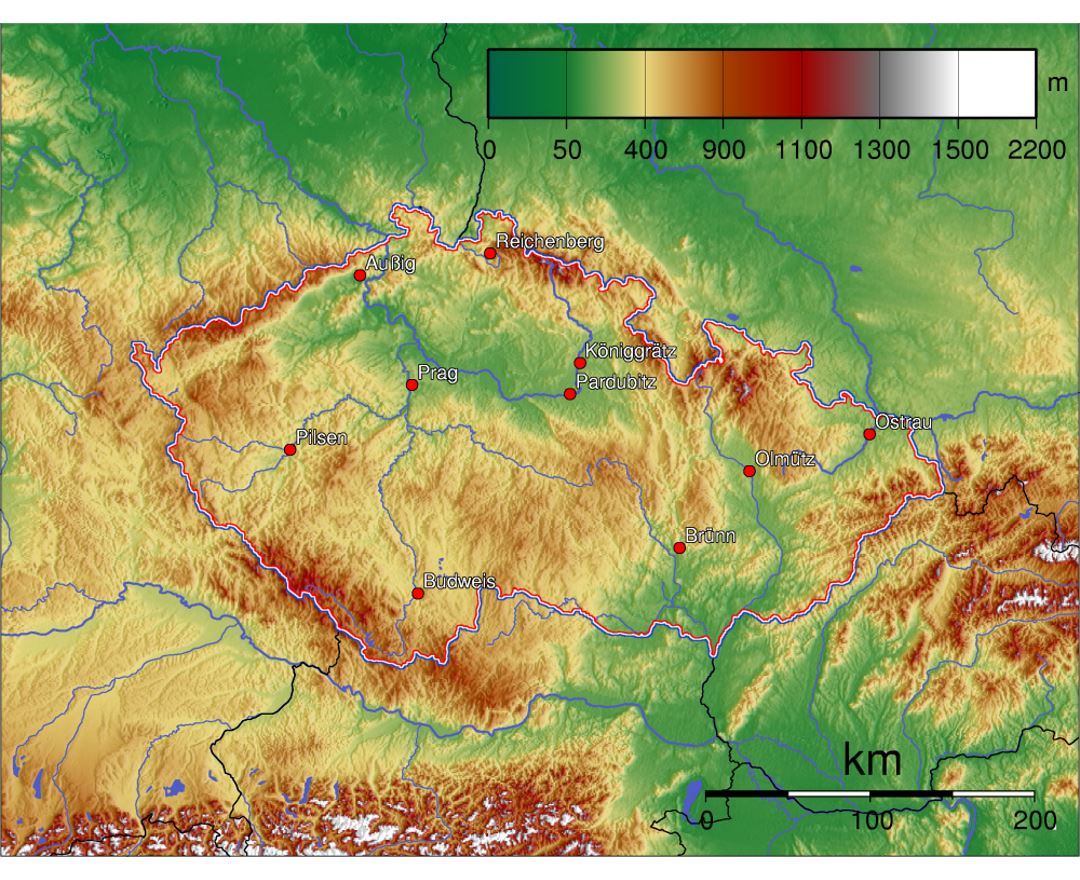
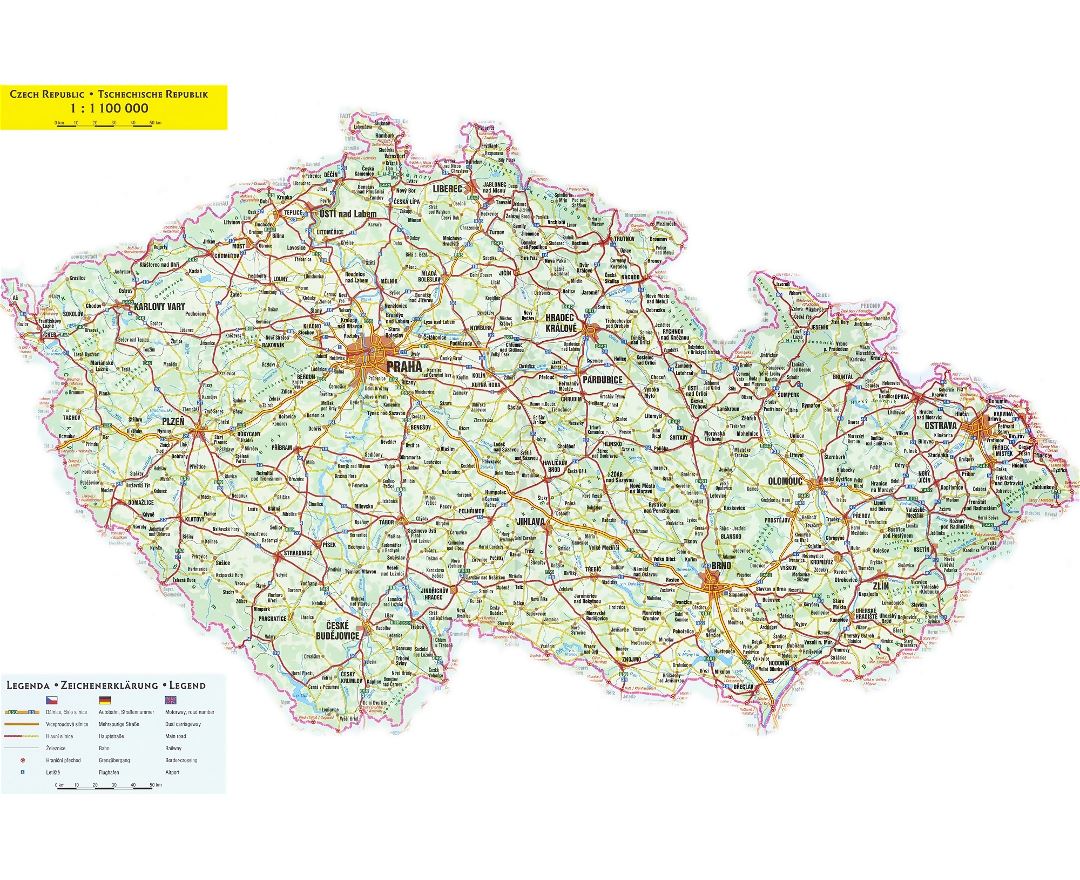
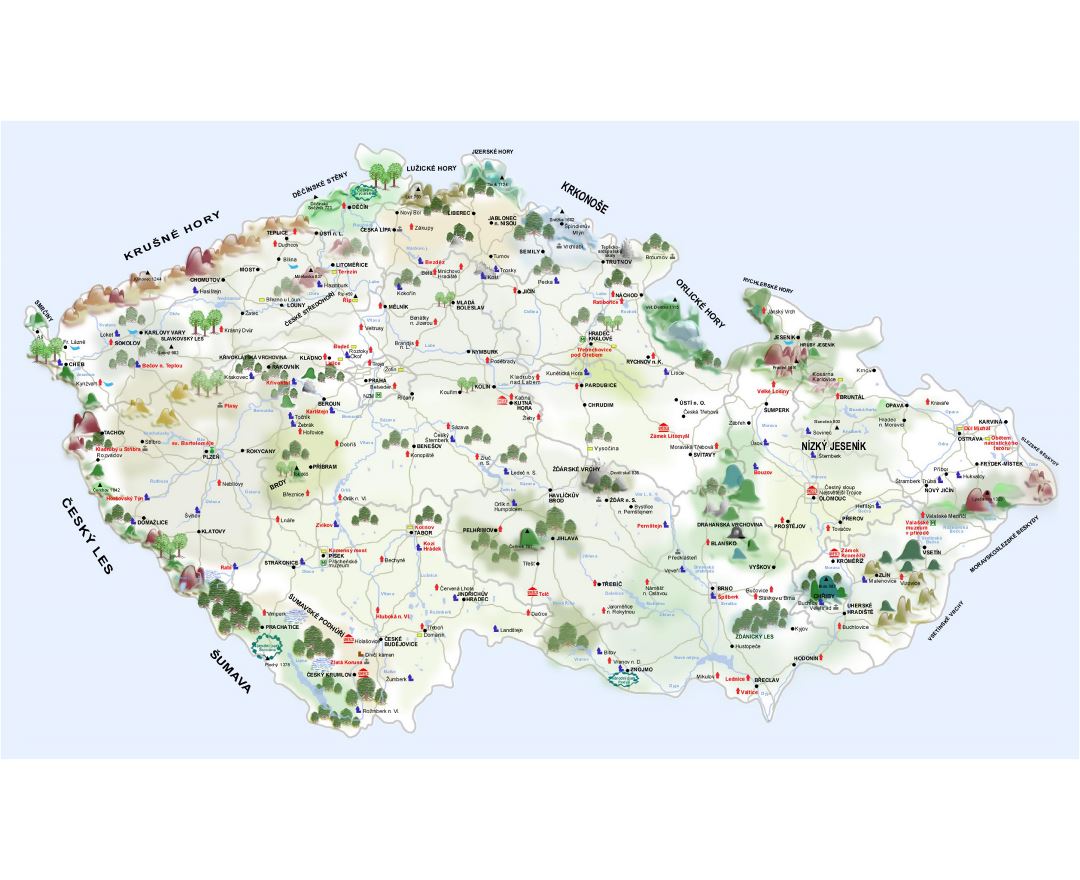
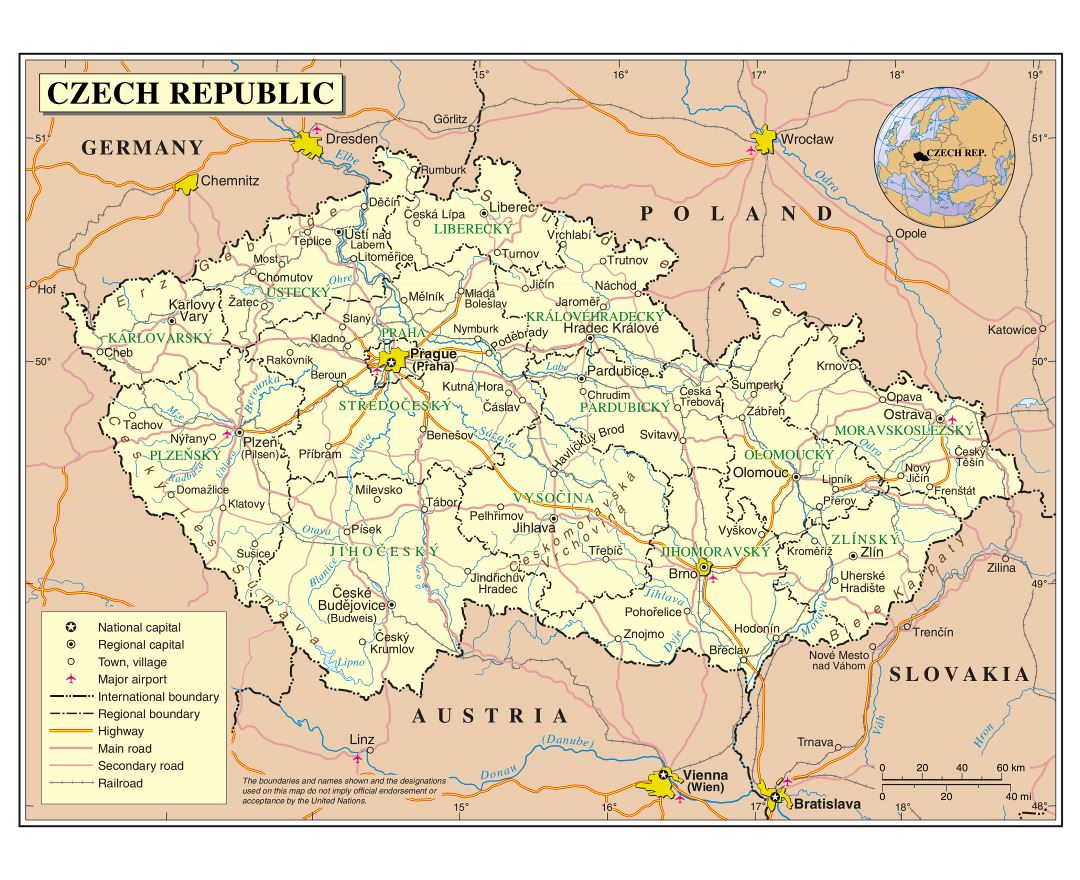
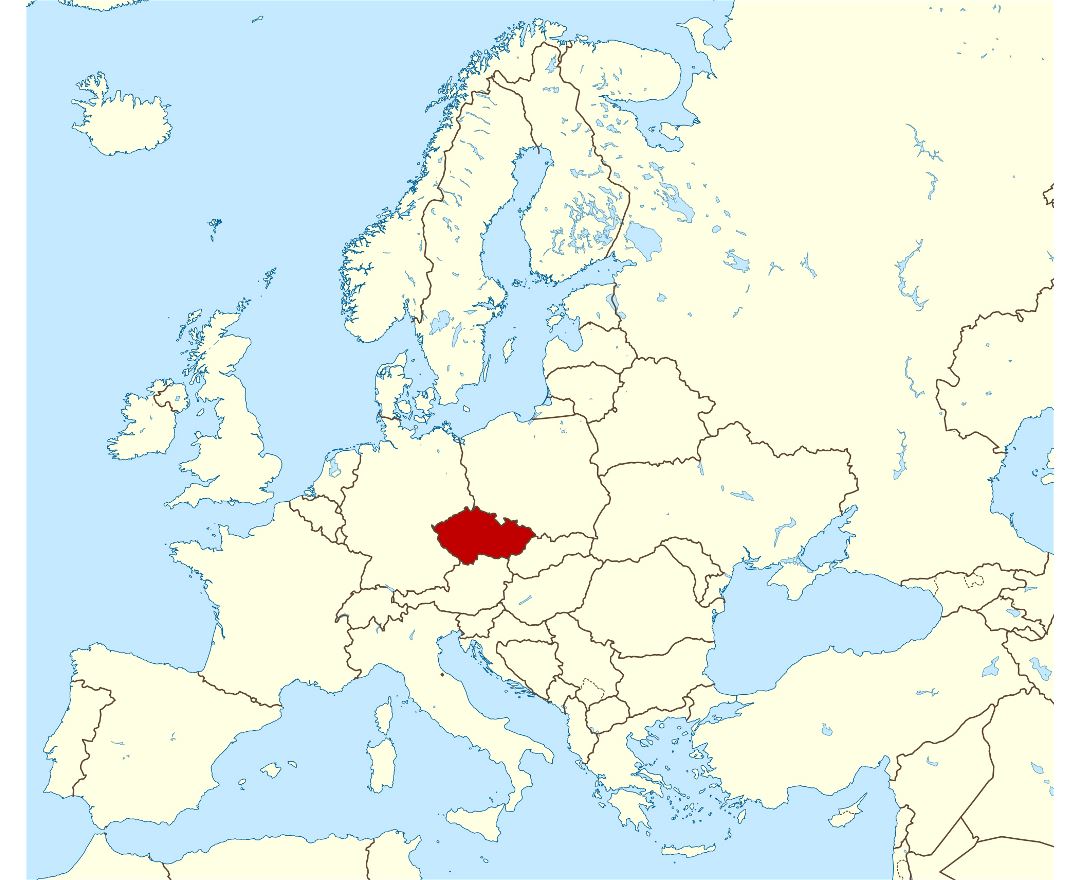
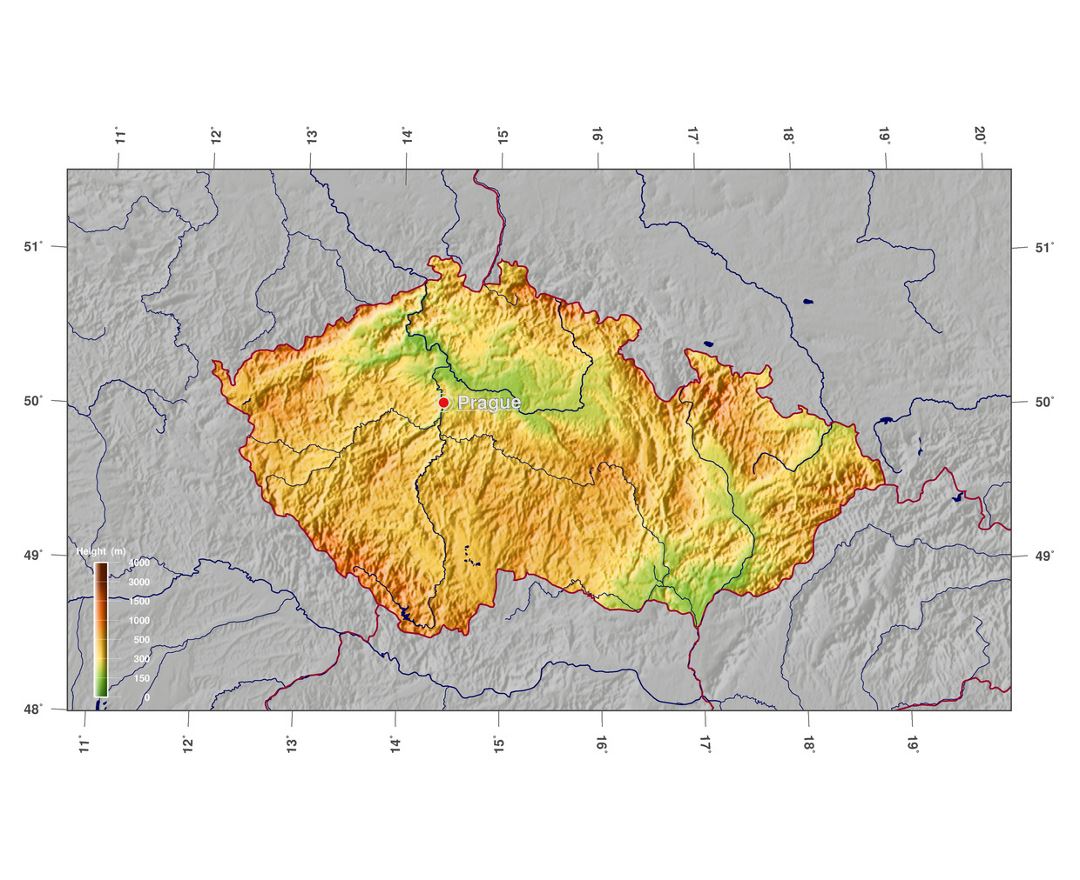
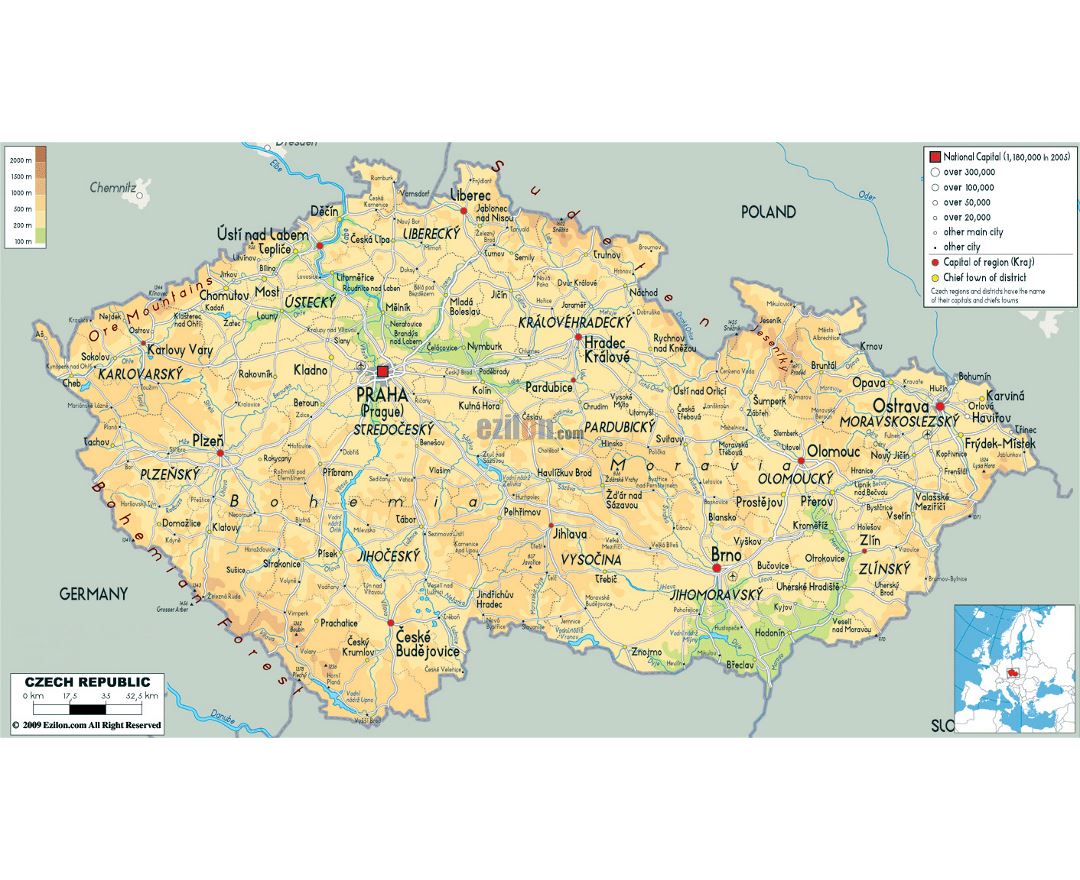
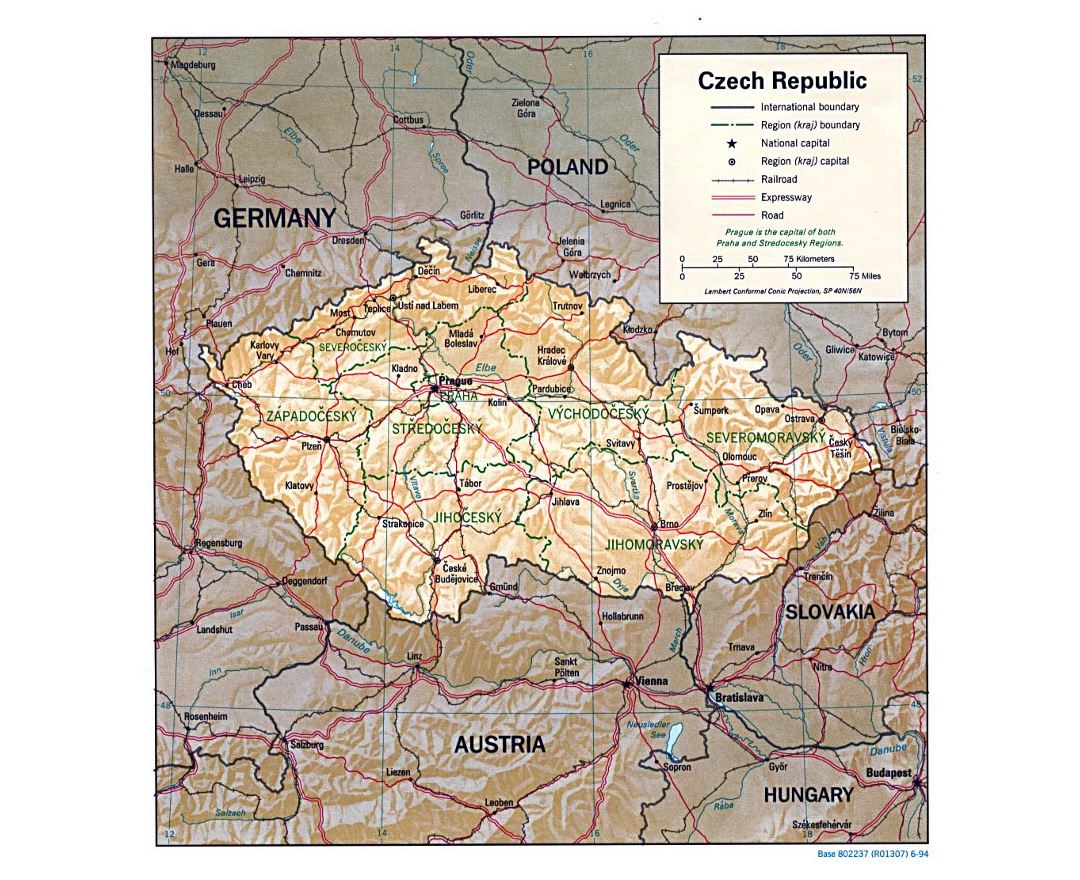
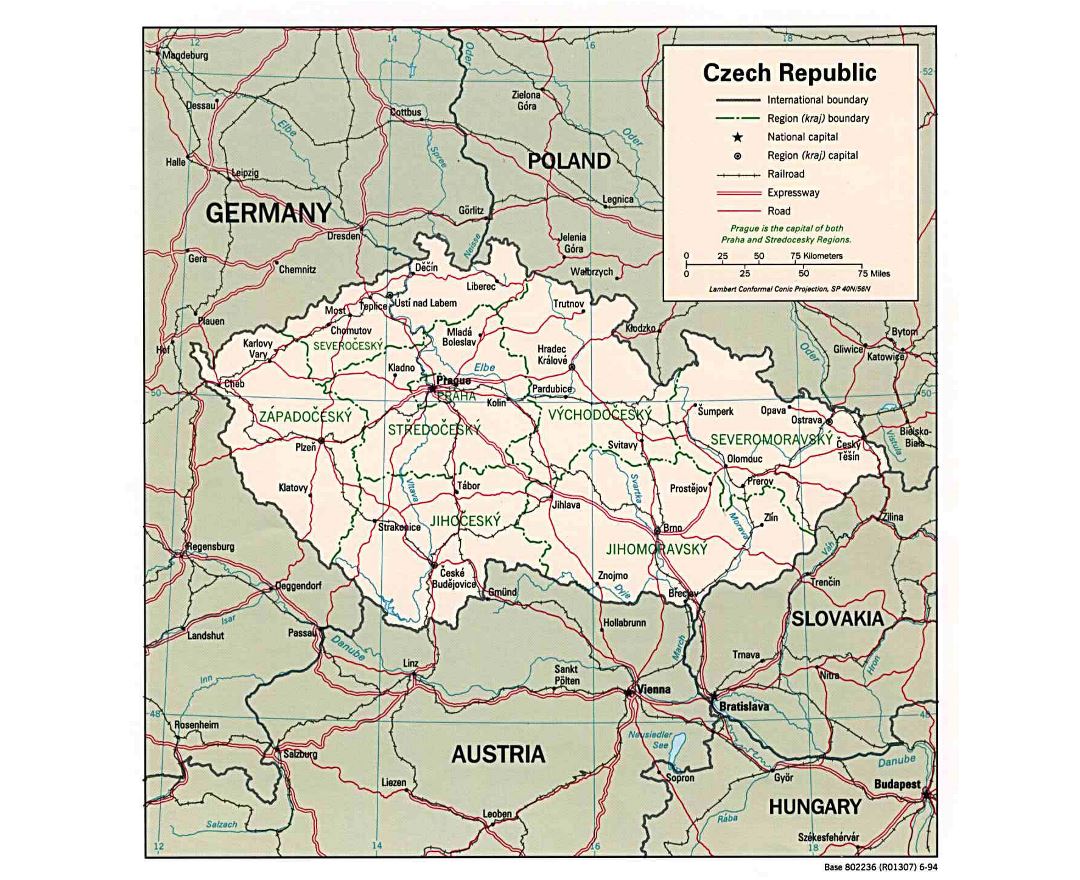
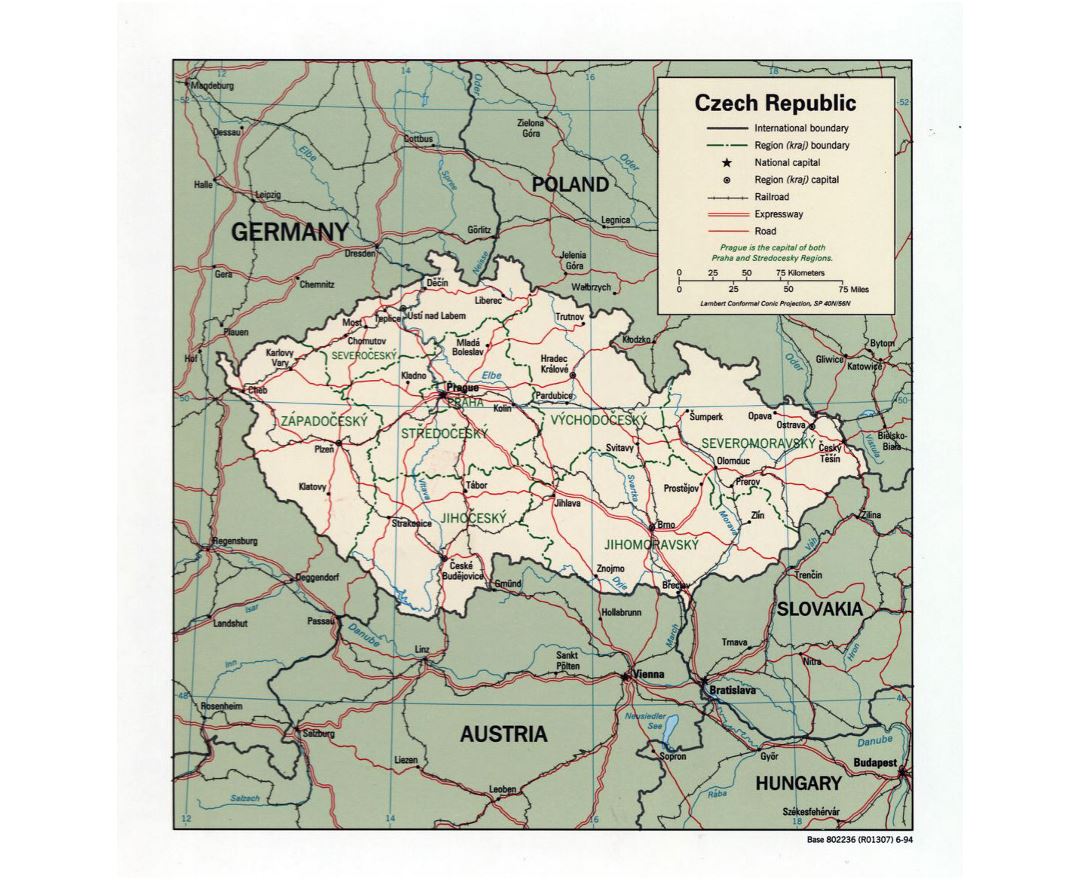
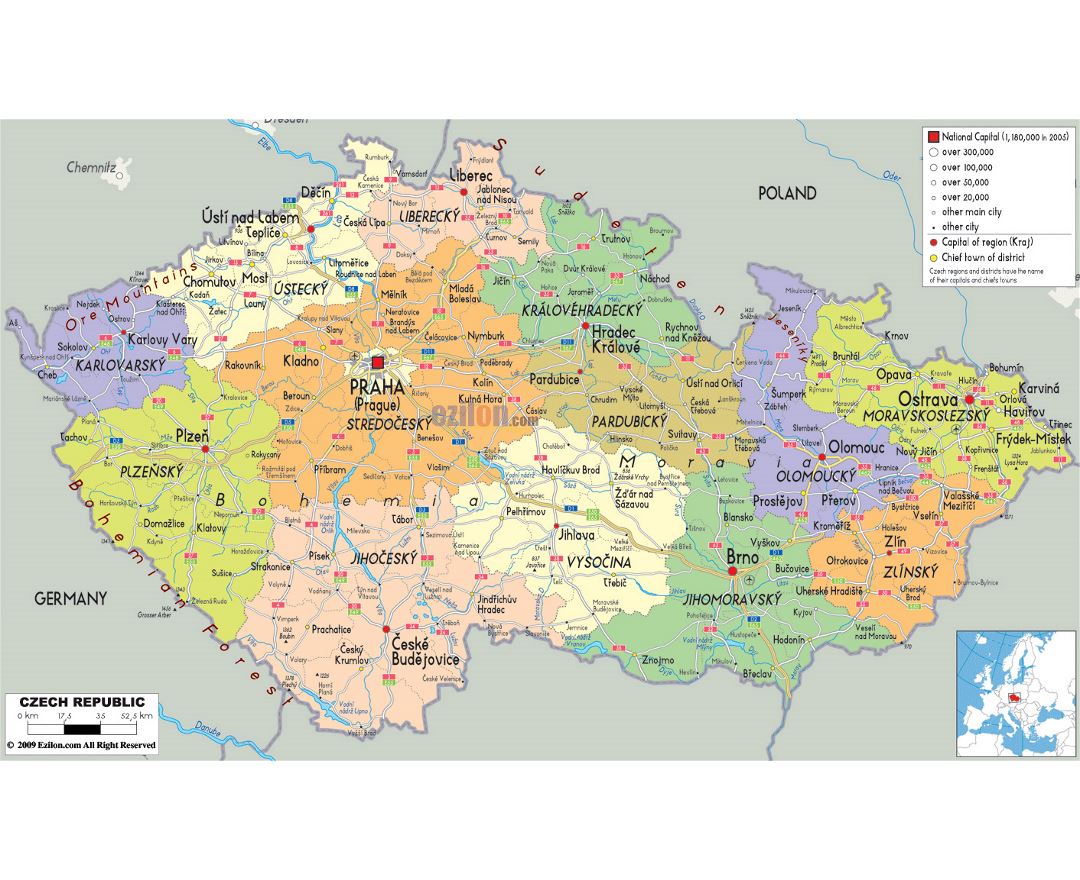
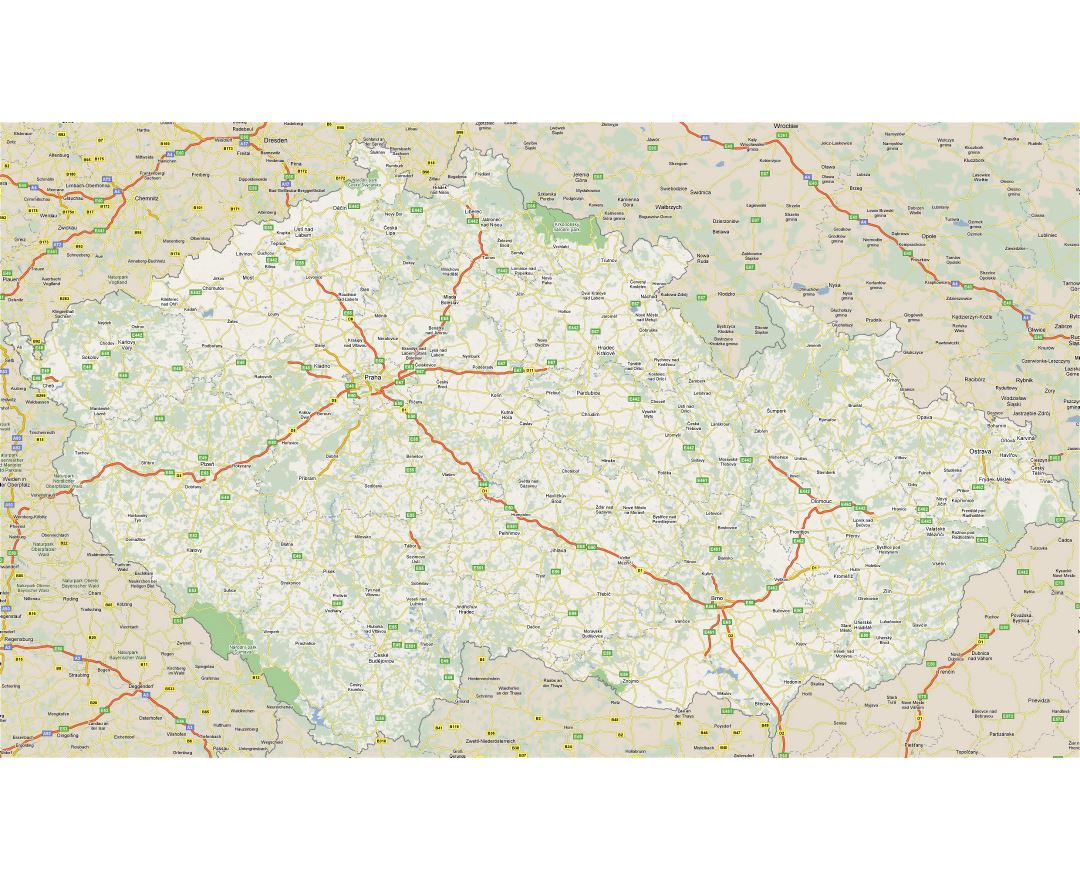
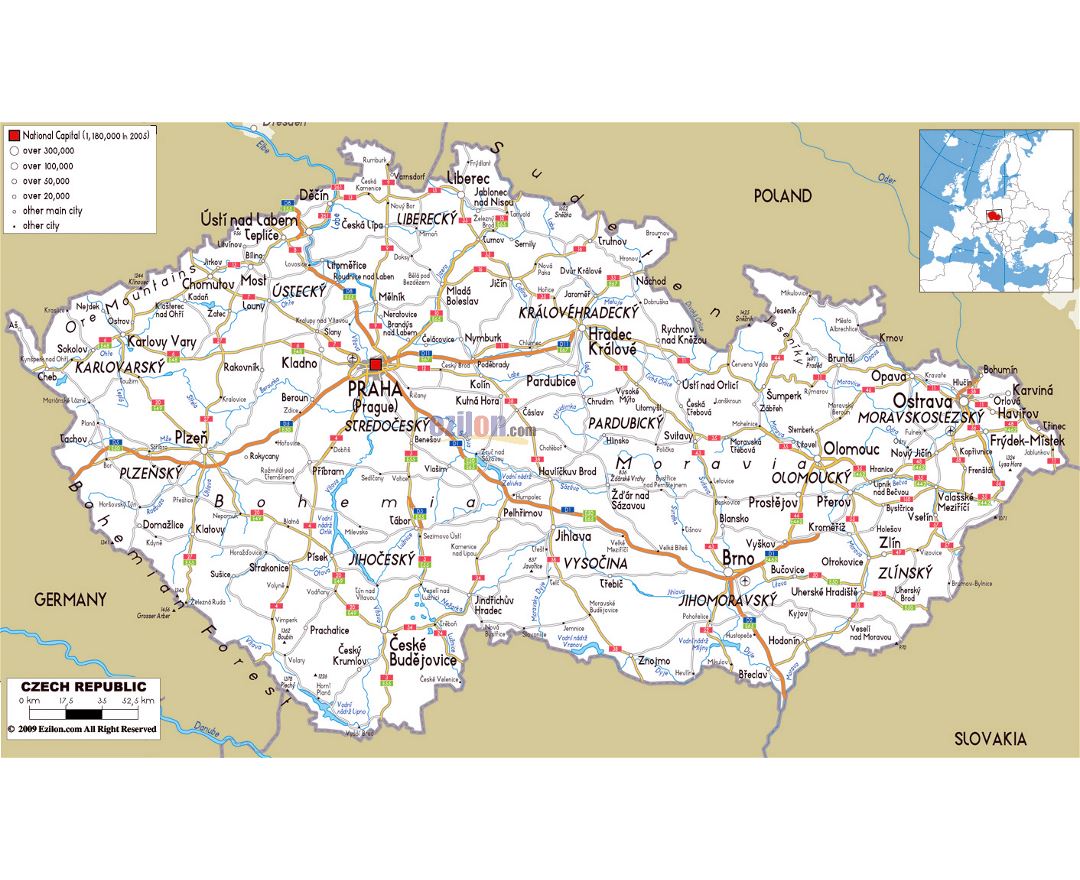
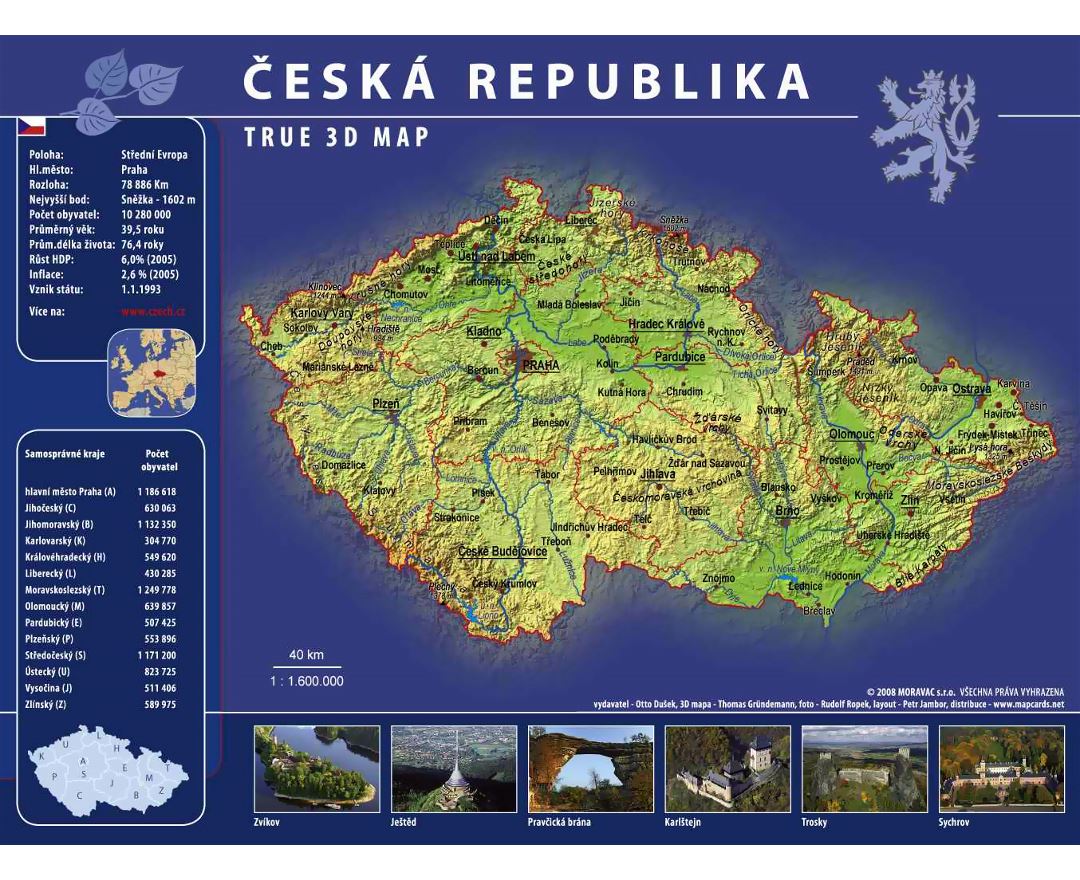
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, is a nation state in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west, Austria to the south, Slovakia to the east and Poland to the northeast. The Czech Republic covers an area of 78,866 square kilometres (30,450 sq mi) with mostly temperate continental climate. It is a unitary parliamentary republic, has 10.5 million inhabitants and the capital and largest city is Prague, with over 1.2 million residents. The Czech Republic includes its historical territories of Bohemia, Moravia, and Czech Silesia.
The Czech state was formed in the late 9th century as the Duchy of Bohemia under the Great Moravian Empire. After the fall of the Empire in 907, the centre of power transferred from Moravia to Bohemia under the Premyslid dynasty. In 1004, the duchy was formally recognized as part of the Holy Roman Empire, becoming the Kingdom of Bohemia in 1198 and reaching its greatest territorial extent in the 14th century. Besides Bohemia itself, the king of Bohemia ruled the lands of the Bohemian Crown, he had a vote in the election of the Holy Roman Emperor, and Prague was the imperial seat in periods between the 14th and 17th century. In the Hussite wars of the 15th century driven by the Bohemian Reformation, the kingdom faced economic embargoes and defeated five crusades proclaimed by the leaders of the Roman Catholic Church.
Following the Battle of Mohacs in 1526, the whole Crown of Bohemia was gradually integrated into the Habsburg Monarchy alongside the Archduchy of Austria and the Kingdom of Hungary. The Protestant Bohemian Revolt (1618–20) against the Catholic Habsburgs led to the Thirty Years' War, after which the monarchy consolidated its rule, reimposed Catholicism, and adopted a policy of gradual Germanization. With the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806, the Bohemian Kingdom became part of the Austrian Empire and the Czech language experienced a revival as a consequence of widespread romantic nationalism. In the 19th century, the Czech lands became the industrial powerhouse of the monarchy and were subsequently the core of the Republic of Czechoslovakia, which was formed in 1918 following the collapse of the Austro-Hungarian Empire after World War I.
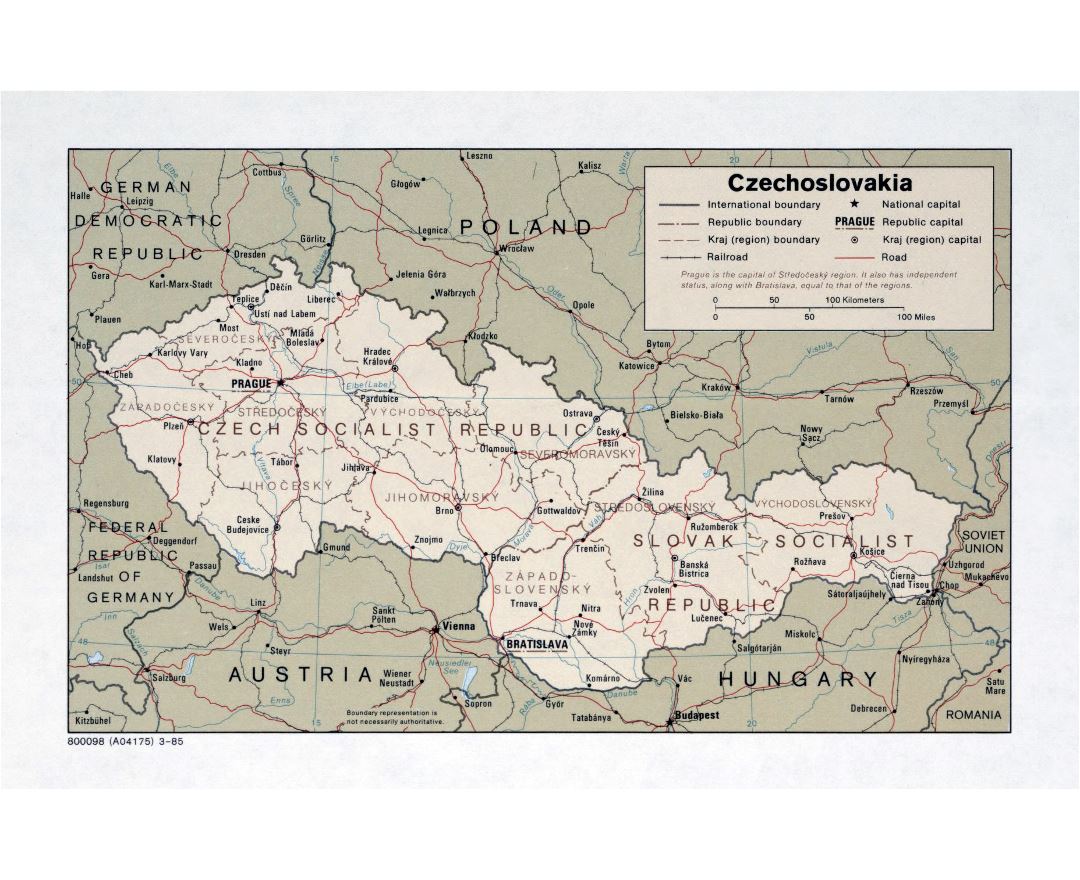
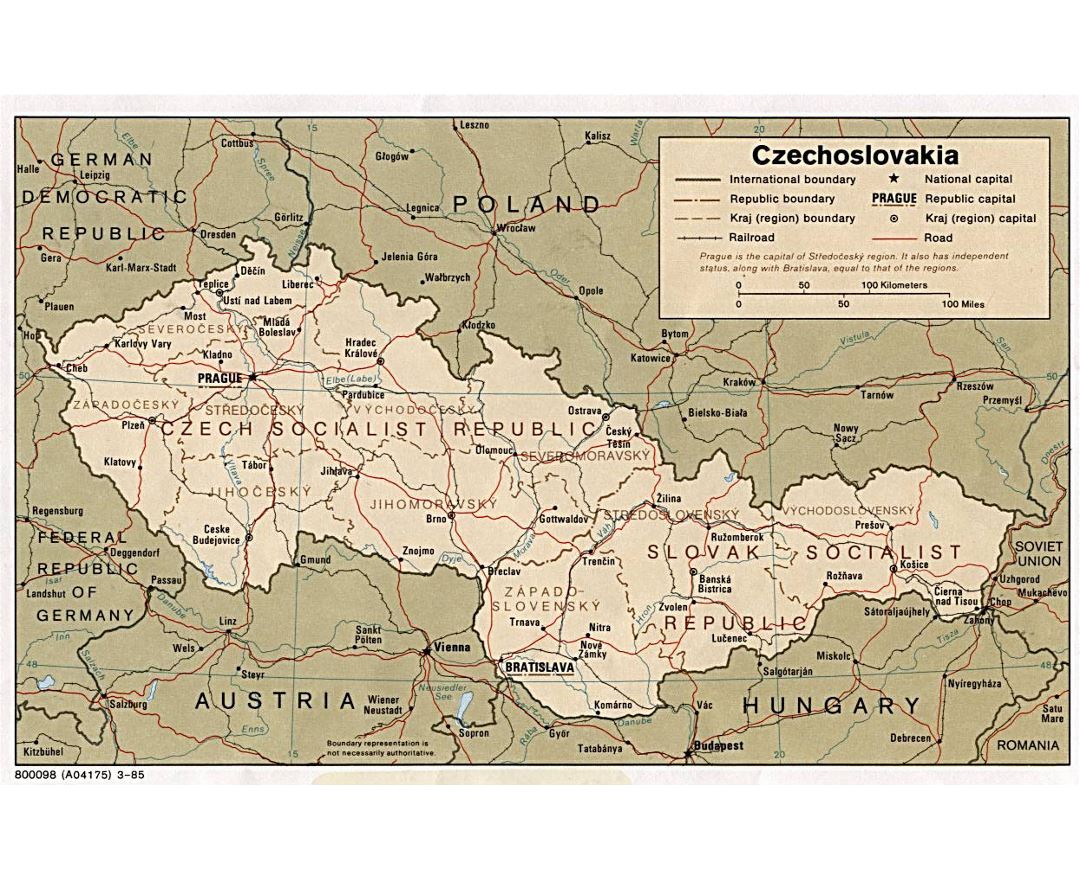
Czechoslovakia was occupied by Germany in World War II, and was liberated in 1945 by the Soviet and the United States armies. Most of the German-speaking inhabitants were expelled after the war and thus the country lost its sizable minority and its bilingual character. The Communist Party of Czechoslovakia won the 1946 elections. Following the 1948 coup d'etat, Czechoslovakia became a one-party communist state under Soviet influence. In 1968, increasing dissatisfaction with the regime culminated in a reform movement known as the Prague Spring, which ended in a Soviet-led invasion. Czechoslovakia remained occupied until the 1989 Velvet Revolution, when the communist regime collapsed and a multiparty parliamentary republic was formed. On 1 January 1993, Czechoslovakia peacefully dissolved, with its constituent states becoming the independent states of the Czech Republic and Slovakia.
The Czech Republic joined NATO in 1999 and the European Union in 2004, it is a member of the United Nations, the OECD, the OSCE, and the Council of Europe. It is a developed country with an advanced, high income economy and high living standards. The UNDP ranks the country 14th in inequality-adjusted human development. The Czech Republic also ranks as the 6th most peaceful country, while achieving strong performance in democratic governance. It has the lowest unemployment rate in the European Union.